"Fuel Cell Vehicles: The Future of Sustainable Motoring?"
What if you could power your car with the most abundant element in the universe, hydrogen? And, what if the only byproduct of this process was water? This isn't a science fiction scenario but the promising reality of fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). The following article will delve into the intriguing world of FCVs, the technology behind them, and their potential impact on the auto industry and environment.
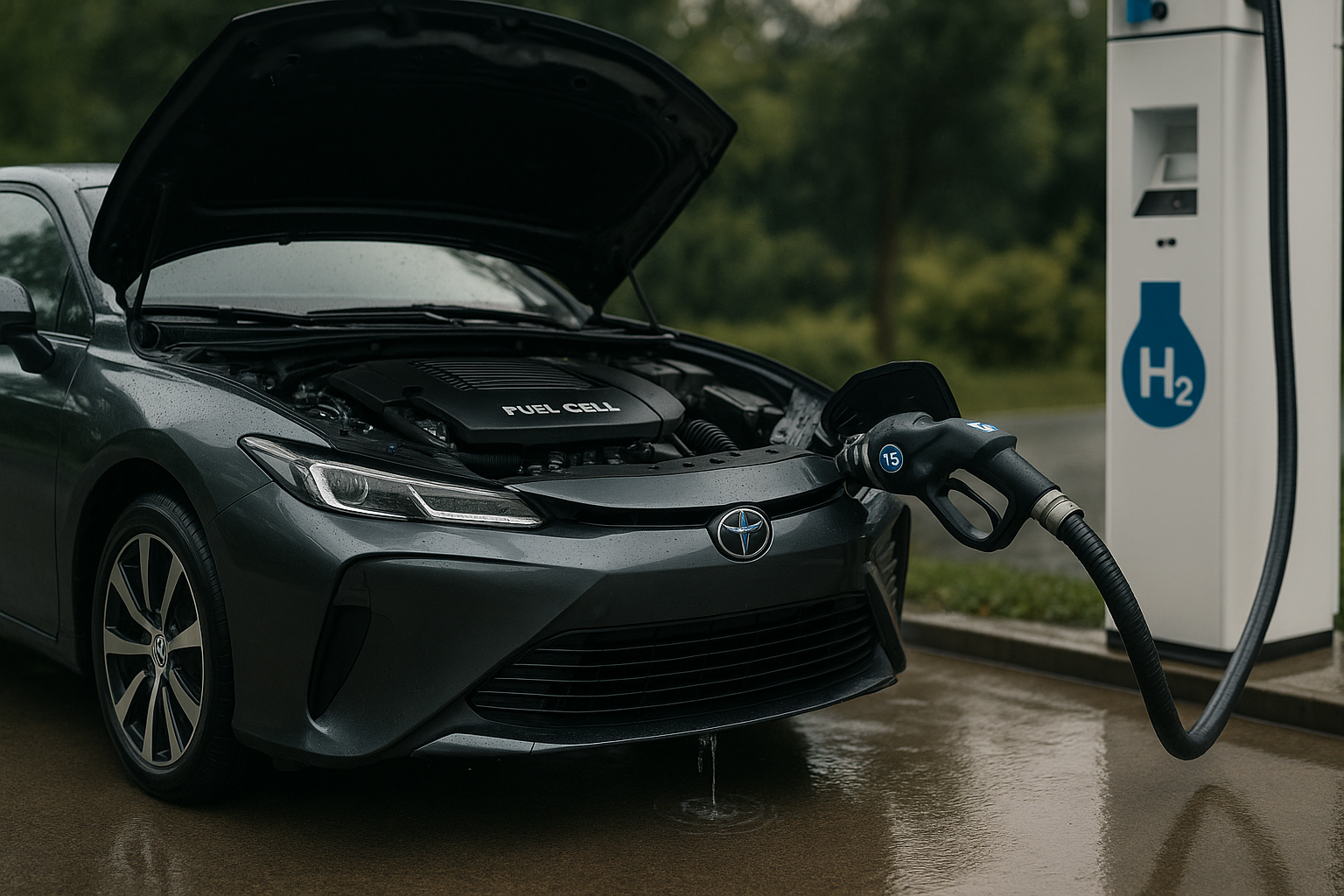

The Science Behind Fuel Cell Vehicles
While the idea of a hydrogen-powered car may seem futuristic, the fundamental technology, fuel cells, has been around since the early 19th century. A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel, in this case, hydrogen, and an oxidizing agent, oxygen, into electricity. In an FCV, the electricity generated by the fuel cell powers an electric motor, which drives the vehicle.
The Advantages of Fuel Cells
One of the major advantages of fuel cells is their high efficiency. While conventional combustion engines are only about 25% efficient, fuel cells can achieve efficiencies of up to 60%. Moreover, since the only byproduct of a hydrogen fuel cell is water vapor, FCVs are zero-emission vehicles and thus a potential solution to the environmental issues posed by conventional cars.
The Challenges Facing Fuel Cell Vehicles
Despite their promise, FCVs face several significant challenges. One of the most daunting is the lack of infrastructure for hydrogen refueling. Building a network of hydrogen stations is a massive and expensive undertaking. Additionally, producing hydrogen in an environmentally friendly way is still a work in progress. Currently, most hydrogen is produced from natural gas, a process that involves carbon emissions.
Fuel Cell Vehicles in the Current Automotive Landscape
Currently, FCVs are a small niche in the automotive market, with only a few models available from manufacturers such as Toyota, Honda, and Hyundai. However, as the industry continues to shift towards sustainable solutions, FCVs are increasingly seen as a promising alternative to both conventional and electric vehicles. In fact, some experts believe that FCVs could ultimately surpass electric vehicles in terms of convenience and environmental benefits.
Conclusion
While it’s too early to say whether fuel cell vehicles will become a mainstay of the automotive industry, they certainly represent an intriguing and potentially transformative technology. As improvements in fuel cell efficiency and hydrogen production methods continue, as well as infrastructure development, FCVs may well be the clean, efficient, and sustainable vehicles of the future.